Does Permify Supports Authentication?
Authentication involves verifying that the person actually is who they purport to be, while authorization refers to what a person or service is allowed to do once inside the system. To clear out, Permify doesn’t handle authentication or user management. Permify behave as you have a different place to handle authentication and store relevant data. Authentication or user management solutions (AWS Cognito, Auth0, etc) only can feed Permify with user information (attributes, identities, etc) to provide more consistent authorization across your stack.How Are Access Decisions Evaluated?
Access decisions are evaluated by stored authorization data and your authorization model, Permify Schema. At a high level, access of a subject is related to the relationships or attributes created between the subject and the resource. You can define this data in Permify Schema then create and store them as relational tuples and attributes, which basically forms your authorization data. Permify Engine computes access decisions in 2 steps,- Looking up authorization model for finding the given action’s ( edit, push, delete etc.) relations.
- Walk over a graph of each relation to find whether given subject ( user or user set ) is related with the action.
edit action. Let’s say we have a model as follows
document:12 belongs, and owners of the document:12 can edit. Permify runs two concurrent queries for parent.admin and owner:
Q1: Get the owners of the document:12.
Q2: Get admins of the organization where document:12 belongs to.
Since edit action consists of or between owner and parent.admin, if Permify Engine finds user:3 in the results of one of these queries then it terminates the other ongoing queries and returns authorized true to the client.
Rather than or, if we had an and relation then Permify Engine waits for the results of these queries before returning a decision.
How To Manage Schema Changes?
It’s expected that your initial schema will eventually change as your product or system evolves. As an example, when a new feature arises and related permissions are created, you need to change the schema (rewrite it with the new permission) then configure it using this Write Schema API. Afterwards, you can use the preferred version of the schema in your API requests with schema_version. If you do not prefer to use schema_version params in API calls Permify automatically gets the latest schema on API calls. A potential caveat of changing or creating schemas too often is the creation of many idle relation tuples. In Permify, created relation tuples are not removed from the stored database unless you delete them with the delete API. For this case, we have a garbage collector which you can use to clear expired or idle relation tuples. We recommend applying the following pattern to safely handle schema changes:- Set up a central git repository that includes the schema.
- Teams or individuals who need to update the schema should add new permissions or relations to this repository.
- Centrally check and approve every change before deploying it via CI pipeline that utilizes the Write Schema API. We recommend adding our schema validator to the pipeline to ensure that any changes are automatically validated.
- After successful deployment, you can use the newly created schema on further API calls by either specifying its schema ID or by not providing any schema ID, which will automatically retrieve the latest schema on API calls.
What is the Preferred Deployment Pattern For Permify?
Permify can be deployed as a sole service that abstracts authorization logic from core applications and behaves as a single source of truth for authorization. Gathering authorization logic in a central place offers important advantages over maintaining separate access control mechanisms for individual applications. See the What is Authorization Service Section for a detailed explanation of those advantages.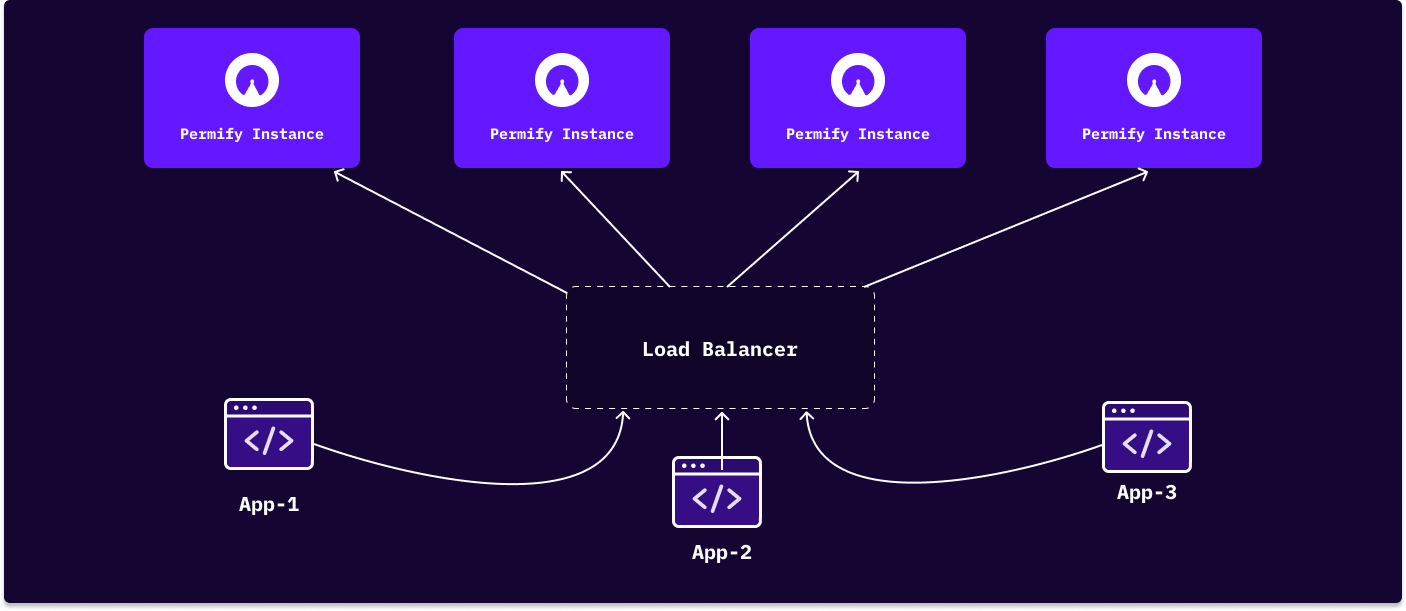 Since multiple applications could interact with the Permify Service on that pattern, preventing bottleneck for Permify endpoints and providing high availability is important.
As shown in the schema above, you can horizontally scale Permify Service by positioning Permify instances behind a load balancer.
Since multiple applications could interact with the Permify Service on that pattern, preventing bottleneck for Permify endpoints and providing high availability is important.
As shown in the schema above, you can horizontally scale Permify Service by positioning Permify instances behind a load balancer.